India’s Caste System Assignment
Tennessee State Standard
6.26 Outline the social structure of the caste system and explain its effect on everyday life in Indian society. (C, E, H, P)
This assignment is basically an essay, but it is set up a bit different than your normal essay. Each paragraph below states exactly what I want in each of your paragraphs. There will be no introduction and no conclusion. Only write the five paragraphs as instructed below. Each paragraph must have a minimum of five (5) sentences. Each sentence must have a minimum of ten (10) words. I will not count words, but I will easily be able to spot sentences with too few words!!!
You must use your Ancient India academic vocabulary whenever possible!!!
Please complete this assignment on Google Docs and make sure to share it with Mr. Barton at bbarton@k12mcs.net when you are ready to turn it in to me!!!
You need to use font size 12 and font style calibri which is what Google docs defaults to when you open it.
NAME YOUR DOC: Lastname.Firstname.Caste (use the first name I know you by)
You will be assigned one of the five divisions of India’s social classes known as the caste system. The five divisions are:
- Brahmins
- Kshatriya
- Vaishya
- Shudra
- Dalit
Your first paragraph will give the history of the caste system or how it came into being in Ancient India.
Your second paragraph will tell what type of people are in each of the five divisions of India’s caste system. This would include priests, laborers, etc. and tell what they do in their job.
Your third paragraph will include how the caste system has helped or harmed the economics in Ancient India and modern India. This would include which of the castes have the most money and which one has the least money and anything in between. In this paragraph you also need to mention two people in India’s history (ancient or modern) who were harmed by the caste system or were helped by the caste system and how.
Your fourth paragraph will include the caste division you were assigned, one of the five above. In detail give who would be in that particular caste system (laborers, farmers, priests), how it corresponds to our social classes (upper, middle, or lower-or even below that), were people in that caste poor, rich, or somewhere in between, could they move into another caste, and give the names of at least two people (ancient or modern) who were/are members of that caste in India and why you chose them or what you found out about them.
Your fifth paragraph is your opinion about what you have just researched. Let me know if you agree/disagree with the caste system and why or why not. Pick out a couple of things you learned that you really disliked/liked and tell me about them and why you disliked/liked them. Let me know a few things you would change if you could and how you would go about changing them (this must be a real-world fix for the problem, you may not say I’d just make the rich give the poor money or I’d wave my magic wand, etc.).
Make sure you include how the caste system influenced India’s culture, their economic system, give some history, and name at least two people in your assigned caste you found info about and some of their history.
Use google to find information about the people and castes. Some search terms examples are as follows.
- India’s caste system
- Any of the five divisions of the caste listed at the top of this page.
- How India’s caste system started
- India caste system Hinduism
- Hinduism caste system
- Ancient India social classes caste
- Or just ask for Mr. Barton’s help
This assignment is easily doable. You must concentrate and actually try on this one. It should be an easy good grade, but if you choose not to do it as assigned, you should not expect to earn a good grade.
Good luck.
The due dates of this paper are as described below.
For my odd classes (3rd, 5th, & 7th periods) at class time on Wednesday, February 1, 2017.
For my even classes (4th, 6th, & 8th periods) at class time on Thursday, February 2, 2017.
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Vocabulary
Subcontinent- a large landmass that is smaller than continent
Monsoon- heavy rain and wind occurring in Southern Asia lasting from July to September, somewhat similar to hurricane season in the U.S., but monsoons occur over the entire subcontinent and are not quite as destructive as a hurricane. Brought on by warm moist air from the Indian Ocean hitting the Himalaya Mountains then rising and the water condensing with the fall in temperature creating heavy rains.
Language Family- a group of similar language (such as Indo-European--meaning the language came from Indian and European influence)
Raja- an Indian prince
Theocracy - a system of government by priests claiming a divine commission.
Sanskrit- the first written language of India; the language ancient Hindu scriptures were written in
Vedas- ancient sacred writings of India
Nirvana - (in Buddhism) a transcendent state in which there is neither suffering, desire, nor sense of self, and the subject is released from the effects of karma and the cycle of death and rebirth. It represents the final goal of Buddhism.
Caste- an Indian social class whose members are restricted in the jobs they may take and in their association with members of other castes; Indian term for caste system is jati
Guru- a teacher
Dharma- a personal duty to one's religion
Hinduism - third largest major religion in the world, brought to India during the Aryan invasions by the Aryans
Brahman - In Hinduism means the highest Universal Principle or Spirit, the Ultimate Reality in the universe. In major schools of Hindu philosophy it is the material, efficient, formal and final cause of all that exists.
Reincarnation - Hindus believe your soul is reborn into another form after you die. This is why they believe in karma during the present life. If you do good things in this life (karma), you will be born into a higher form in the next life (human, elephant, tiger). If you do bad things in this life, you will be born into a lower form in the next life (rat, cockroach) to pay for what you did.
Karma - the sum of a person's actions in this and previous states of existence, viewed as deciding their fate in future existences; doing good deeds gives one good karma
Bhagavad Gita - The Bhagavad Gita, often referred to as simply the Gita, is a 700-verse Hindu scripture in Sanskrit that is part of the Hindu epic Mahabharata.
Buddhism - Form of religion that originally began in India during the rule of the Mauryan Empire in Ancient India
Stupas - a dome-shaped structure erected as a Buddhist shrine
Jainism - ancient religion from India that teaches that the way to liberation [freedom] and bliss [happiness] is to live a life of harmlessness and renunciation [not wishing for material goods]. The aim of Jain life is to achieve liberation of the soul.
Plateau- a broad flat area of high land
Reside- to live
Abandon- to leave and not return
Promote - support or actively encourage
Focus - the center of interest or activity
Migrate- to move from one place to another
Emerge- to come into being or become known
Eventual - occurring at the end of or as a result of a series of events; final; ultimate
Decline - a gradual and continuous loss of strength, numbers, quality, or value
Contribute - give (something, especially money) in order to help achieve or provide something
Text- words written down in a particular form, such as a book
Manual- work done by hand
Sacred - holy or considered holy
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Cartography (Mapping) Assignment
You have two maps. One is of the Eastern Hemisphere and the other is of South Asia. One is marked near the top of the page and the other near the top right of the page, so make sure you know which one is which!!! USE ONLY LIGHT COLORS TO COLOR YOUR MAP, NO DARK COLORS AND DO NOT PRESS TOO HARD WITH THE COLORING PENCILS OR IT WILL DESTROY YOUR LABELING!!! Follow the directions given below for each map. Make sure to read them completely as I will take off points for the wrong color being used or for dark colors being used. This time NEATNESS ON YOUR MAP WILL BE PART OF YOUR GRADE!!! Color to the best of your ability and write where everyone can read it easily, not sloppily. The best 5 maps from each class will get five points extra credit and will be placed in the hallway near Mr. Barton’s room for all to see. If I have more than 5 exceptional maps in one class, I will give extra credit to them all and place them all in the hallway. You can use the pull down map in the front of the class and the map of India on the front board. You can also use the provided maps at the bottom of these instructions. If needed, you may google maps of India or South Asia to help you also.
The Eastern Hemisphere Map:
- Write your name, the date, and your period number over modern Russia in the space provided. DO NOT GO TO STEP TWO UNTIL YOU HAVE DONE THIS.
- With a YELLOW pencil or highlighter, fill in the box next to the words Ancient Mesopotamia and then color Ancient Mesopotamia on the map with the same color. Remember what the word Mesopotamia actually means and stay in the area where it really was.
- Under the map in the space provided, write the name of the two major rivers in Mesopotamia.
- Using a light green pencil or a green highlighter, fill in the box next to the words Ancient Egypt, and then with that same color, color the area on the map where Ancient Egypt actually was remembering it was right on the river and did NOT go as far South as Ancient Nubia.
- In the space provided under the map, write the name of the major river in Egypt.
- With a light blue colored pencil or highlighter, fill in the box next to the words Ancient Israel. Now with the same color, color the area where Ancient Israel was located.
- In the space under the map, write the name of the major river located in Ancient Israel.
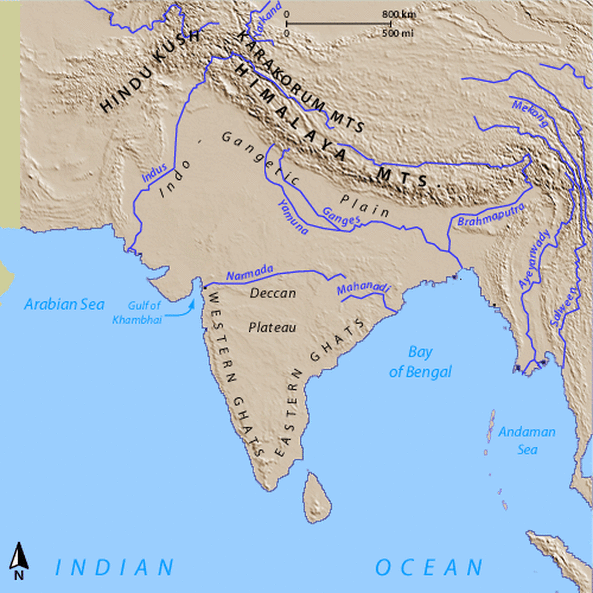
- Using a light Pink colored pencil or highlighter, fill in the box next to the words Ancient India. Now go to the map and color in where Ancient India was located. Remember ancient civilizations ONLY occur on rivers, so stay near the rivers. Ancient India was located on two different rivers and near the river deltas. Mark the area for both rivers.
- On the blank provided under the map, list the two MAJOR rivers in Ancient India. India has more than two rivers, but only two of them are considered major rivers. Only two rivers are shown on the Eastern Hemisphere map, so only list those two.
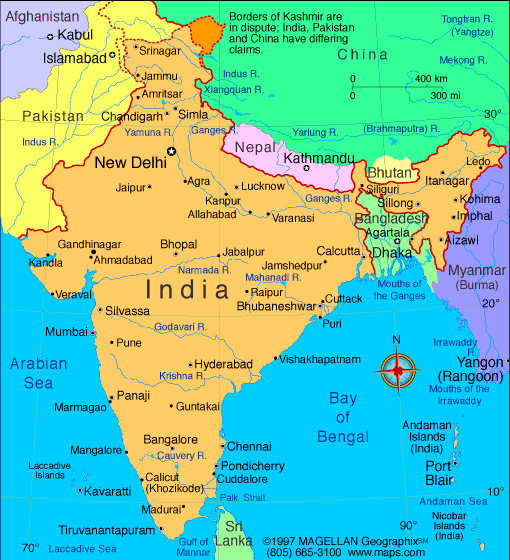
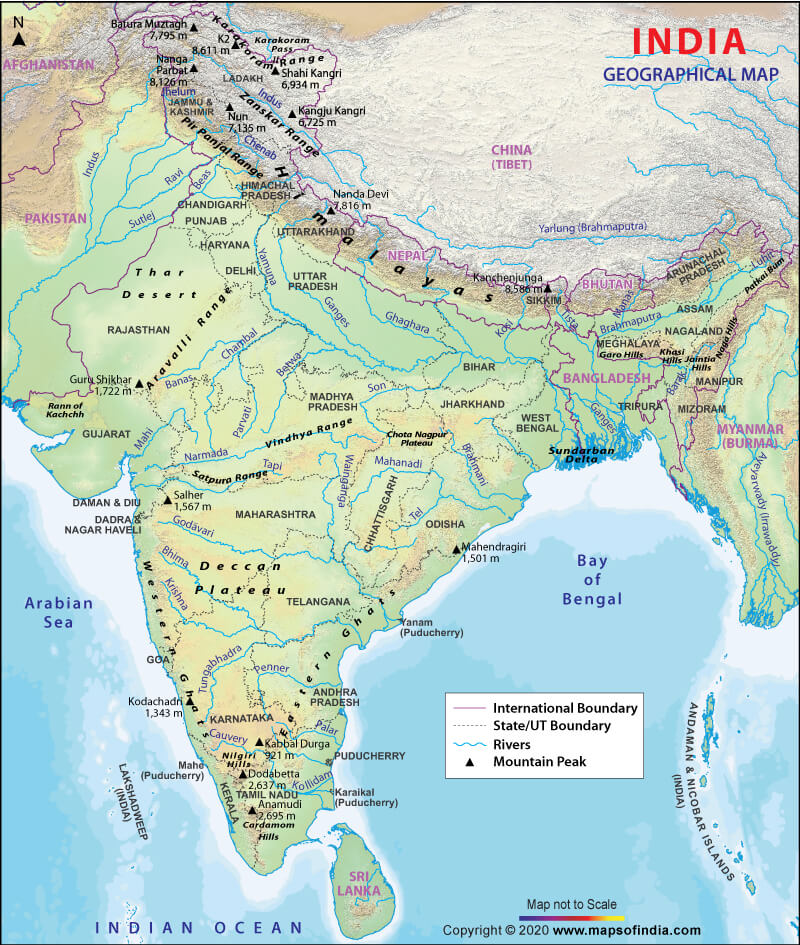
The South Asia Map:
- Write your name, date, and period in the space provided at the top right of the map. DO NOT GO TO STEP TWO UNTIL YOU COMPLETE THIS ACTIVITY!!!
- ONLY use a normal #2 pencil or black colored pencil to label the map.
- In the bottom right corner of the map, draw a compass rose with only the four cardinal points.
- On the South side of the map, on the Equator, label the Indian Ocean.
- To the West of India, label the Arabian Sea.
- To the East of India, label the Bay of Bengal
- Label the Indus River and trace over it with a light blue colored pencil.
- Label the Ganges River and trace over it with a light blue colored pencil.
- With a brown colored pencil draw ^^^^^^^^s where the Himalaya Mountains are located, being careful to not put them on top of the Plateau of Tibet, then label the mountains and the Plateau of Tibet.
- With a light tan or yellow colored pencil, lightly fill in the area where the Great Indian Desert (a.k.a. Thar Desert) is located, then label it.
- Near the mouth of the Indus River, lightly label where Ancient India was located.
- Label the Eastern Ghats.
- Label the Western Ghats.
- Label the Krishna River and trace over it lightly with a blue pencil.
- Label the Godavari River and trace over it in light blue.
- Label the Narmada River and trace over it in light blue.
- With a light green colored pencil or highlighter, trace over the modern borders of Pakistan, India, and Nepal (these are the lines that are dash dot dash or --.--.--. on your map) then label each of the three modern countries.
- Label the modern country of Sri Lanka.
Link to good map (you may need to copy/paste in into your url bar):
http://www.mapsofworld.com/india/

You are now finished. Rejoice!!!